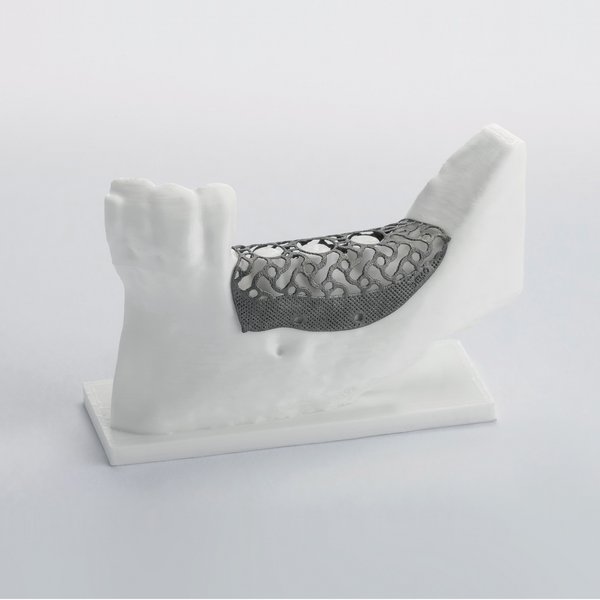
Yxoss CBR®
Customized Bone Regeneration: A new era in dentistry.
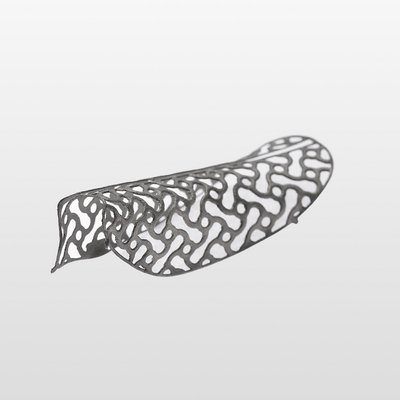
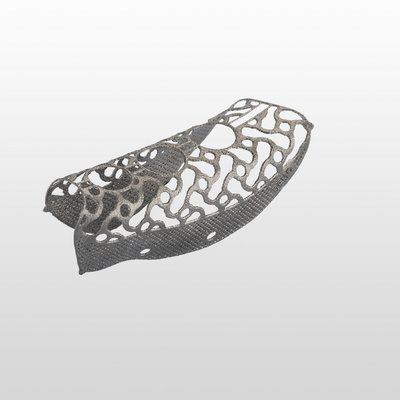
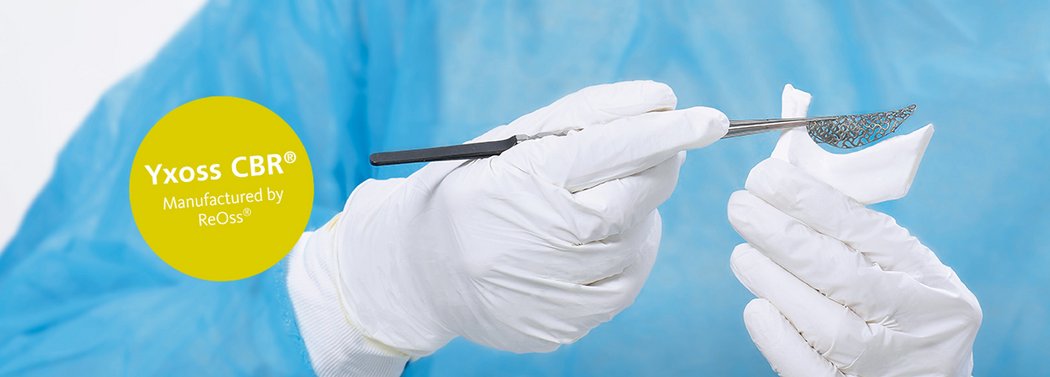
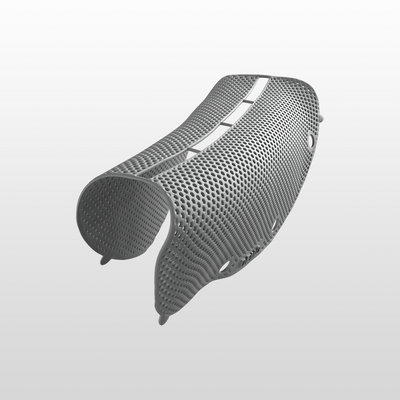
Yxoss CBR®, manufactured by ReOss® GmbH, is a breakthrough technology in Guided Bone Regeneration (GBR), introducing the first customized 3D-printed titanium mesh for treating complex alveolar bone defects.
This innovative solution leverages the patient's CBCT data and a fully digital workflow to create a form-stable scaffold for GBR that perfectly matches their unique anatomy.
With Yxoss CBR®, dentists and oral surgeons can skip the traditional steps of taking impressions, cutting, shaping, and adapting mesh materials to fit the patient's mouth. This saves time and ensures a smoother and safer procedure, without any sharp edges and reduced risks of infection after exposure as the traditional titanium meshes or non-resorbable membranes.
Three options to best suit your needs
Clinically, your needs will vary based on the position and extent of the defect, the patient's anatomy, overall treatment requirements and your own preference. Discover the unique product features and related services you can benefit from.
- Calculation of augmentation volume.
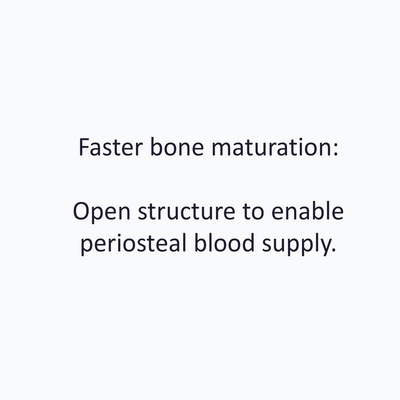
- High stability and space maintenance.
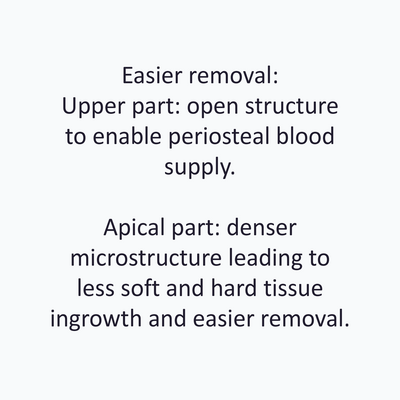
- Easy Removal Design®: pre-defined occlusal breaking points for easy removal on re-entry.
- Yxoss CBR® backward (optional): unique integrated implant positioning in the surgical planning.
Your go-to solution for GBR and beyond
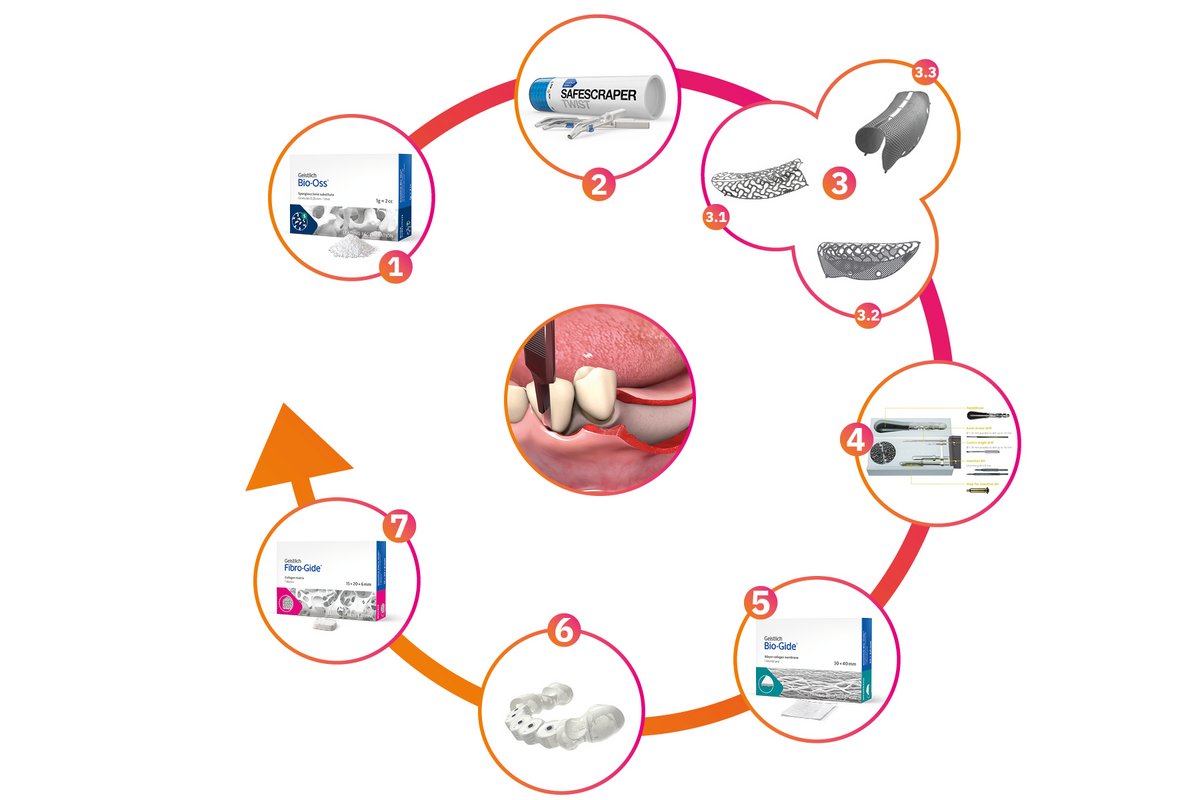
Our biomaterials and solutions for regenerating hard and soft tissues, combined with our exclusive partnership with ReOss® GmbH, manufacturer of Yxoss CBR®, allow us to offer you a complete and convenient solution for GBR of major bone defects and implant placement.

References:
- Data on file. Based on the number of units currently sold. (Wolhusen, Switzerland).
- Orsini G et al.: Oral Dis 2007; 13 (6), 586-93.
- Rothamel D et al.: Clin Oral Implants Res 2005; 16 (3), 369-78.
- Schwarz F et al.: Clin Oral Implants Res 2008; 19 (4), 402-15.
- European Patent Specification – EP 3 055 000 B1.
- Huber S et al.: J Clin Periodontol 2018; 45 (4), 504-12.
- Thoma D et al.: J Clin Periodontol. 2020; 47 (5), 630-39.
- Thoma DS et al.: J Clin Periodontol 2016; 43 (10), 874-85.
- Zeltner M et al.: J Clin Periodontol 2017; 44 (4), 446-53.