Major Bone Augmentation

Scientific background
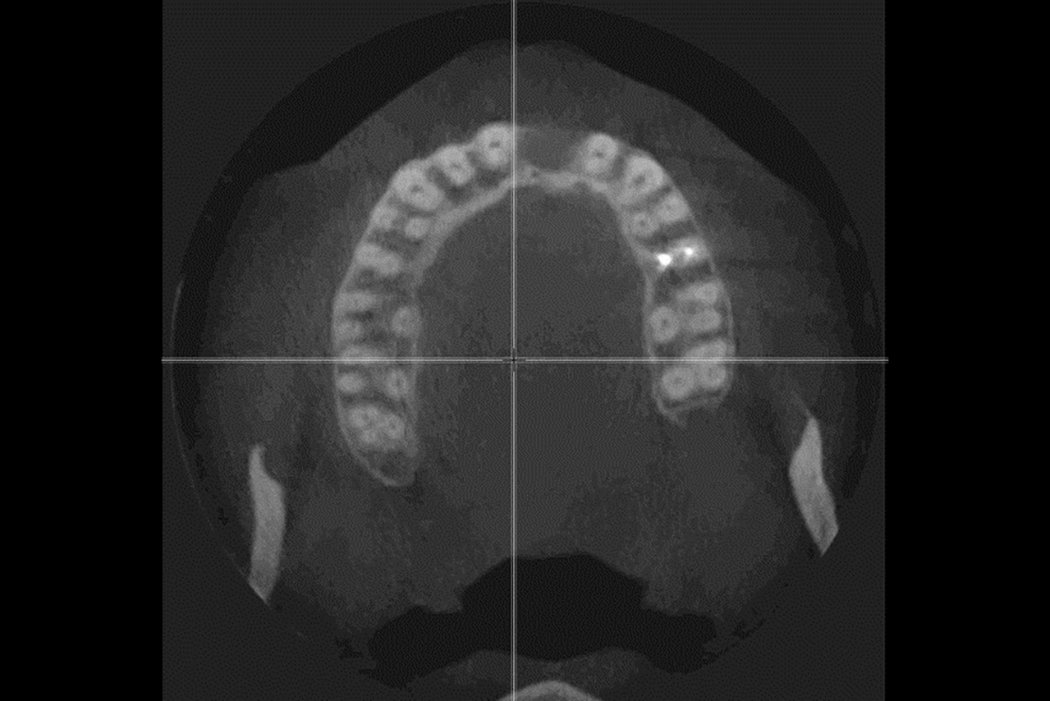
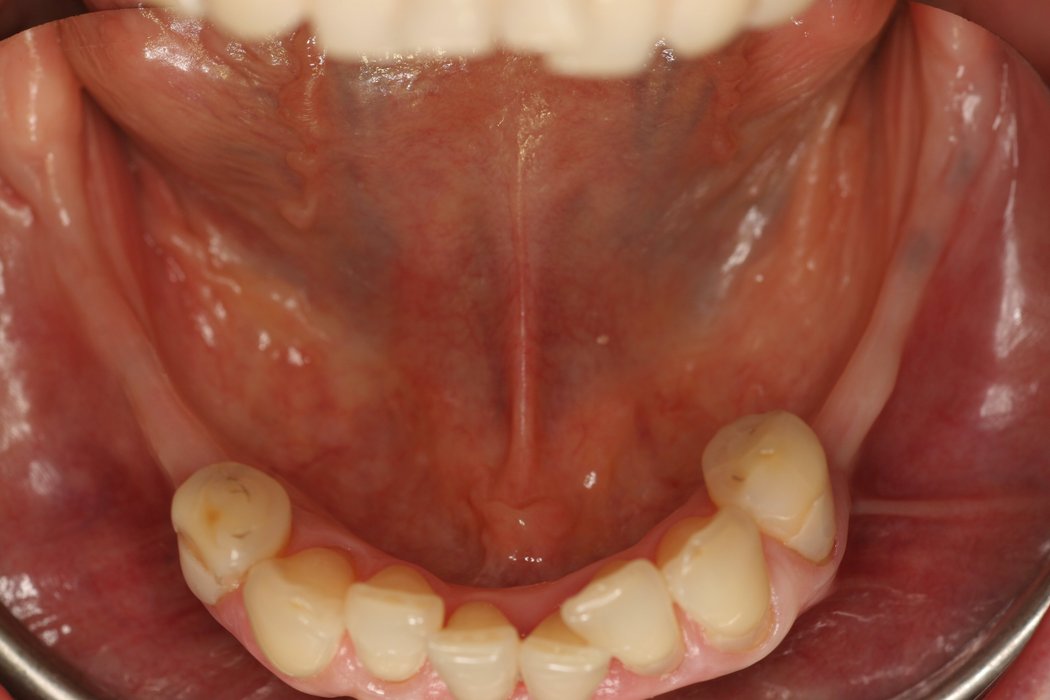
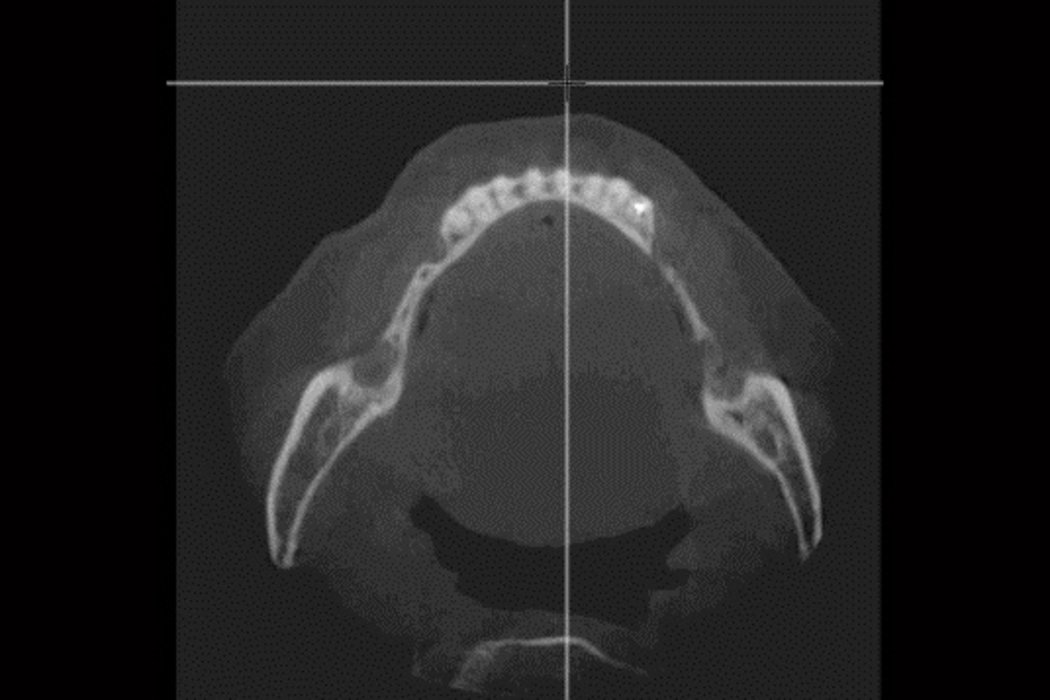
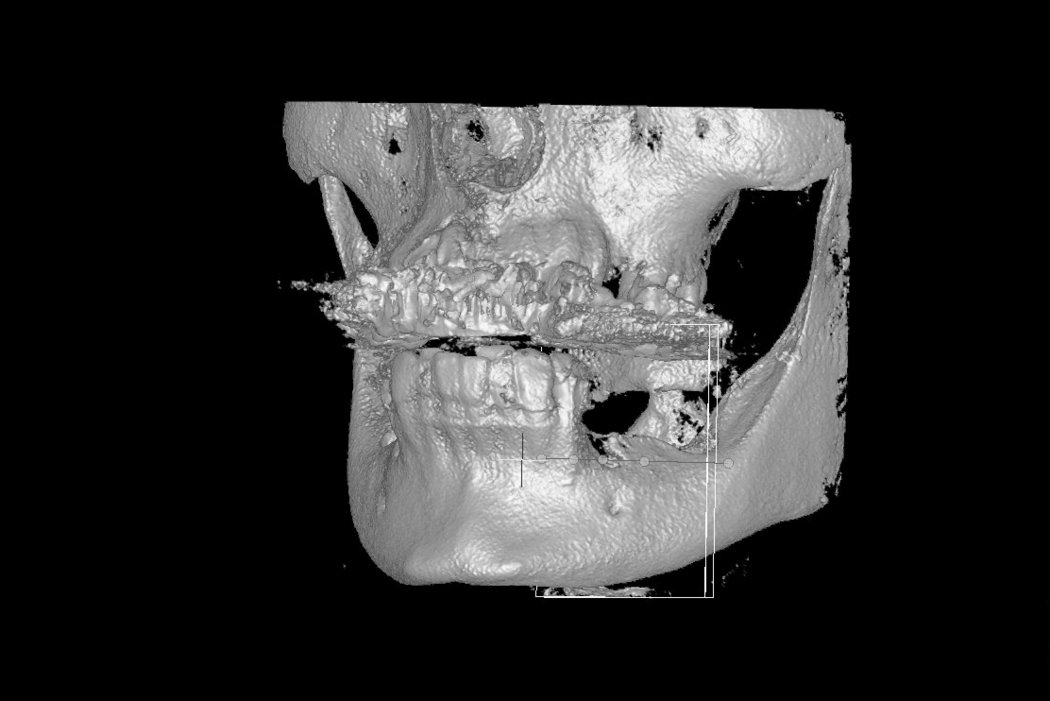
Tooth loss, trauma or tumour resection can lead to large bone deficiencies in the alveolar ridge. Reconstructive measures are indicated to augment poor bone quantity.
Autogenous bone blocks harvested from the lower jaw or the iliac crest are the prevailing material used to reconstruct larger ridge defects. However, autogenous bone blocks are subject to a certain degree of resorption1,2.
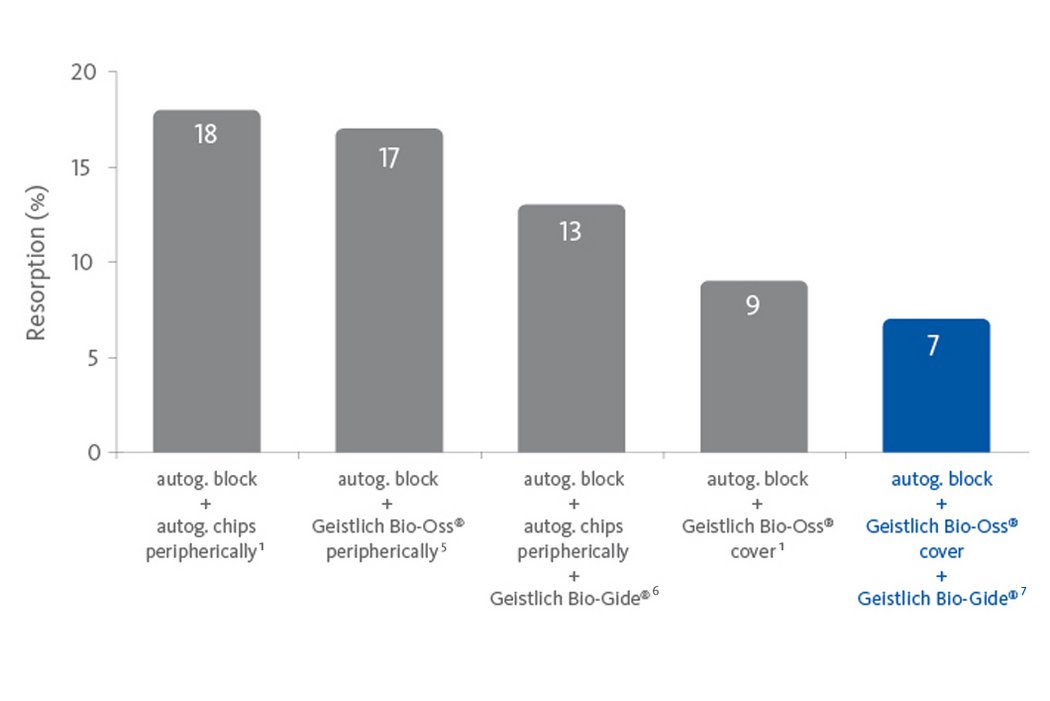
Application of Geistlich biomaterials to a bone block graft diminishes resorption
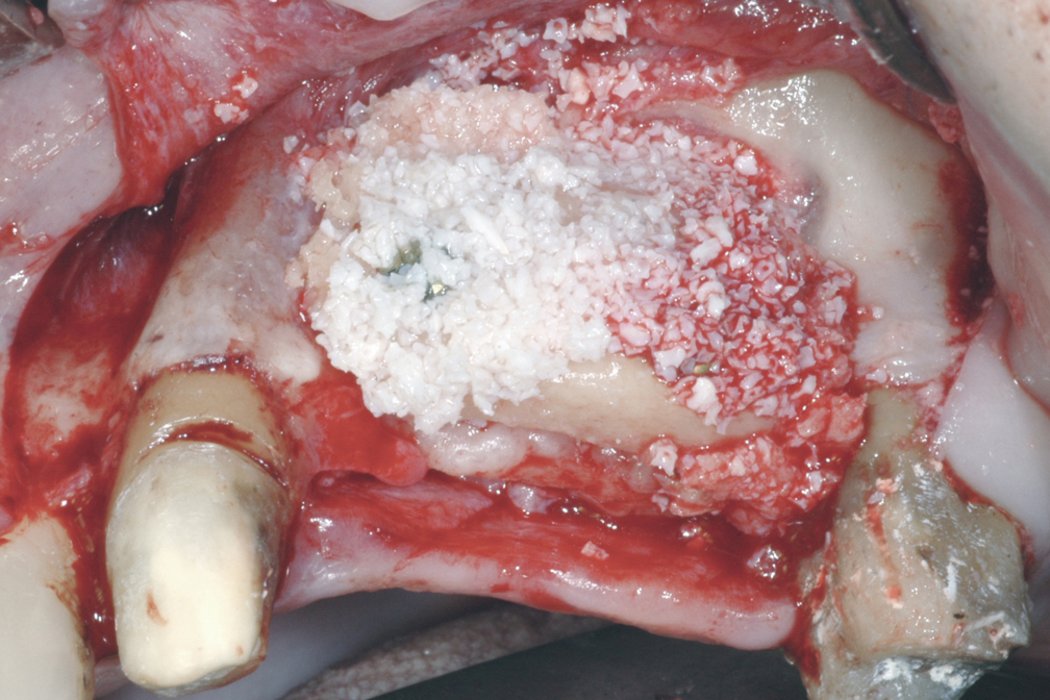
- Geistlich Bio-Oss® bone substitute placed over the graft reduces shrinkage3,4.
- Geistlich Bio-Gide® collagen membrane covering the augmented area further decreases hard tissue resorption1,2,5-7.
Combining autogenous bone with Geistlich Bio-Oss® and Geistlich Bio-Gide® better preserves augmentation in the long term.
References:
- Maiorana C, et al. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2005 Feb;25(1):19–25 (Clinical study).
- Maiorana C, et al.: Open Dent J. 2011 Apr 25;5:71-8 (Clinical study).
- Schlegel KA et al.: Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2003 Jan–Feb;18(1):53–8 (Preclinical study).
- Jensen T et al., Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012 Mar;23(3):263–73 (Clinical study).
- Proussaefs P, et al.: Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2002; 17(2): 238-48 (Clinical study).
- Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2006 Feb;26(1):43-51 (Clinical study).
- von Arx T, Buser D: Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006 Aug;17(4):359–66 (Clinical study).
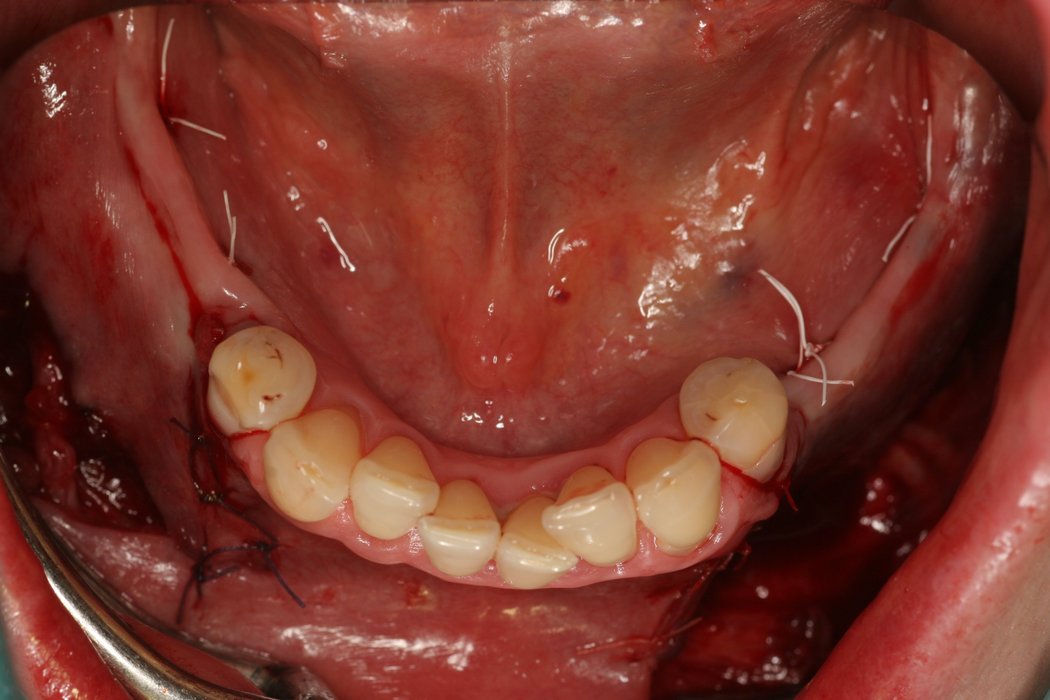
Clinical Cases
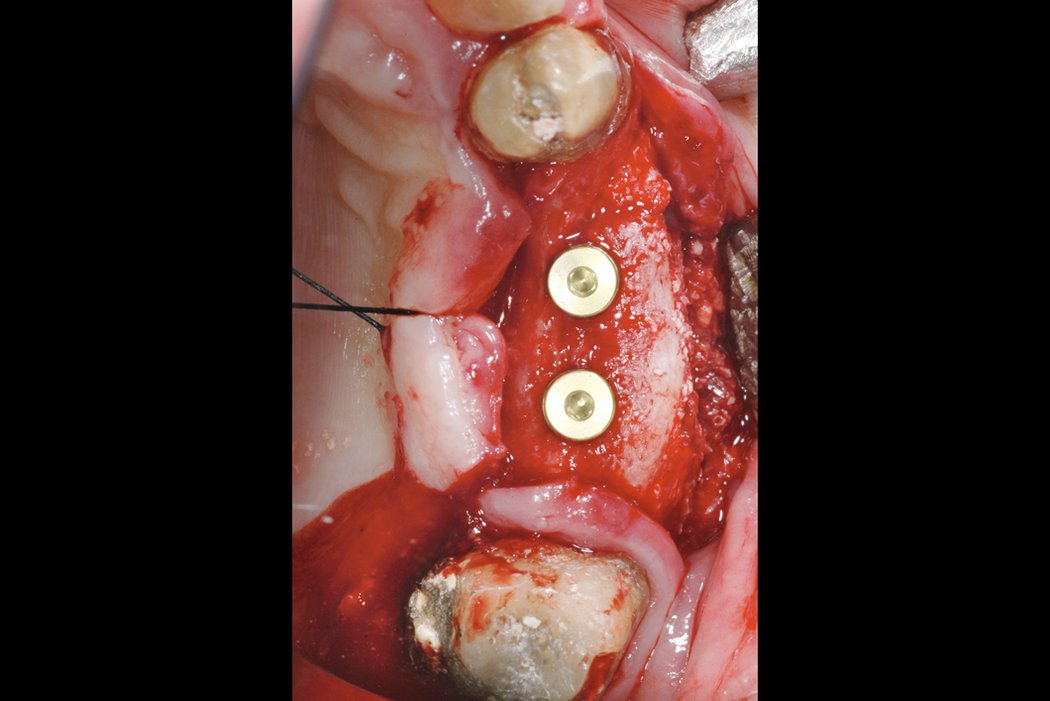
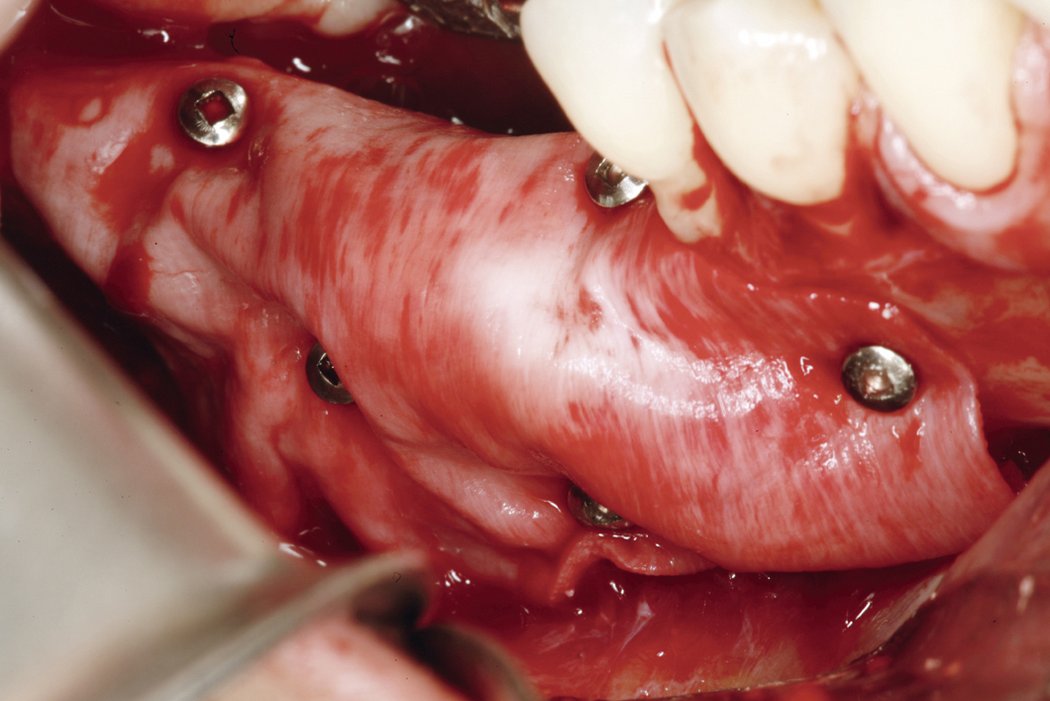
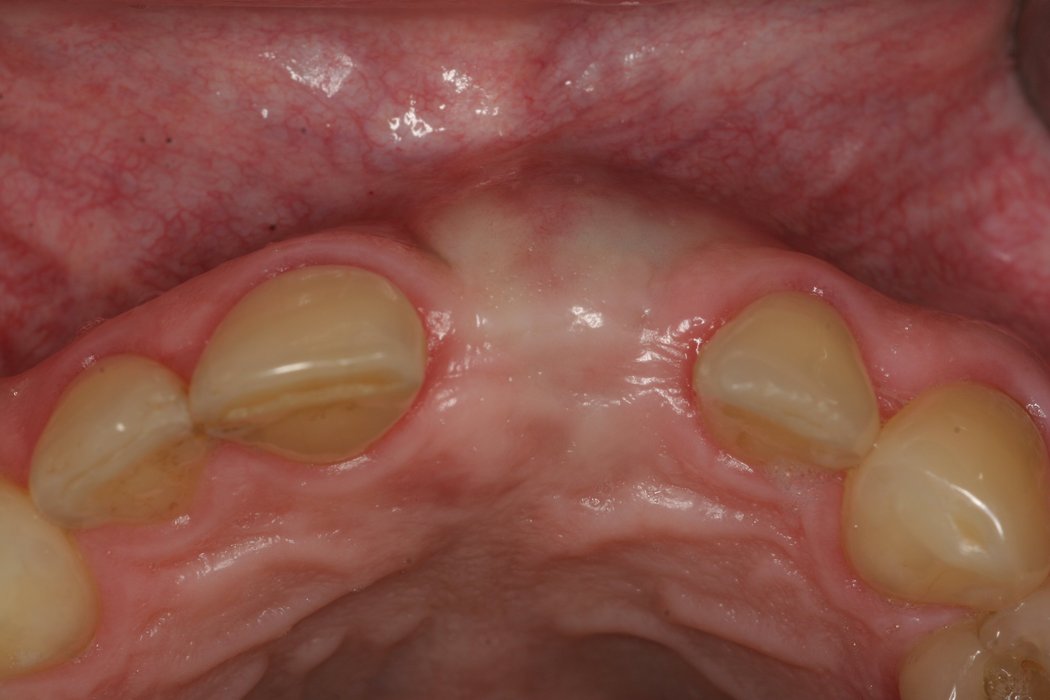
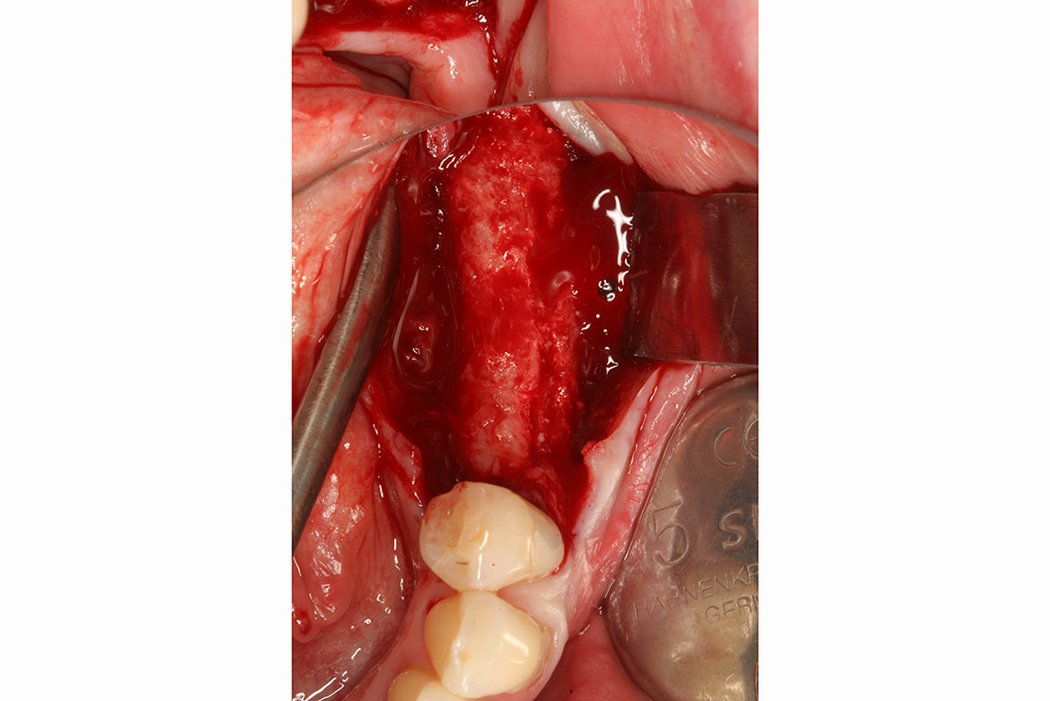
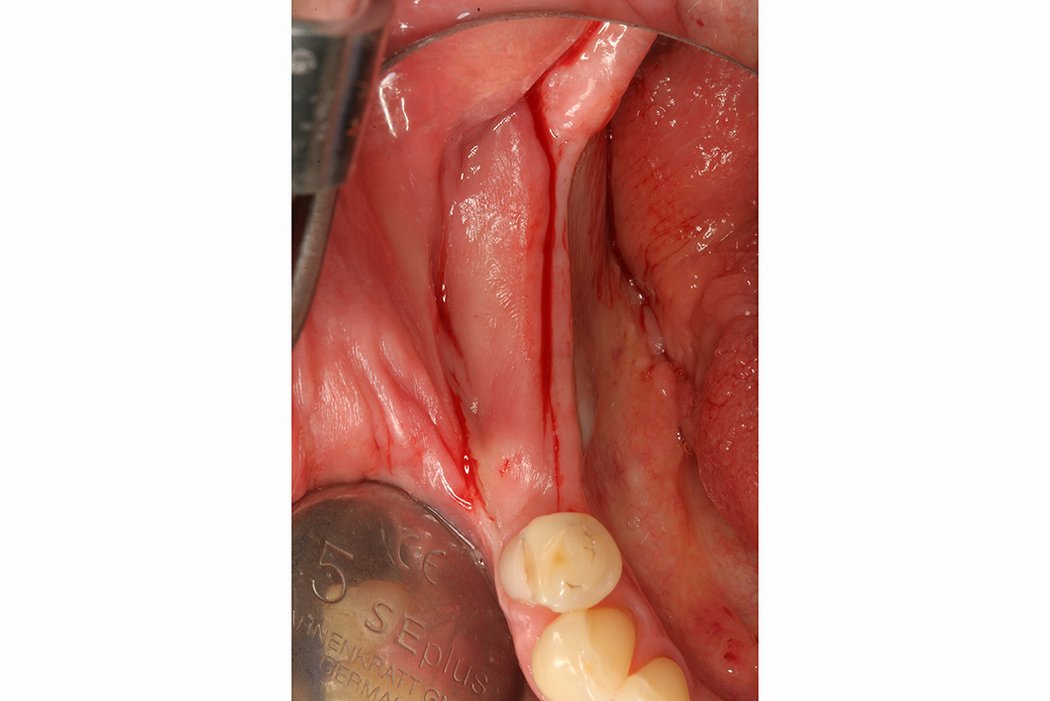
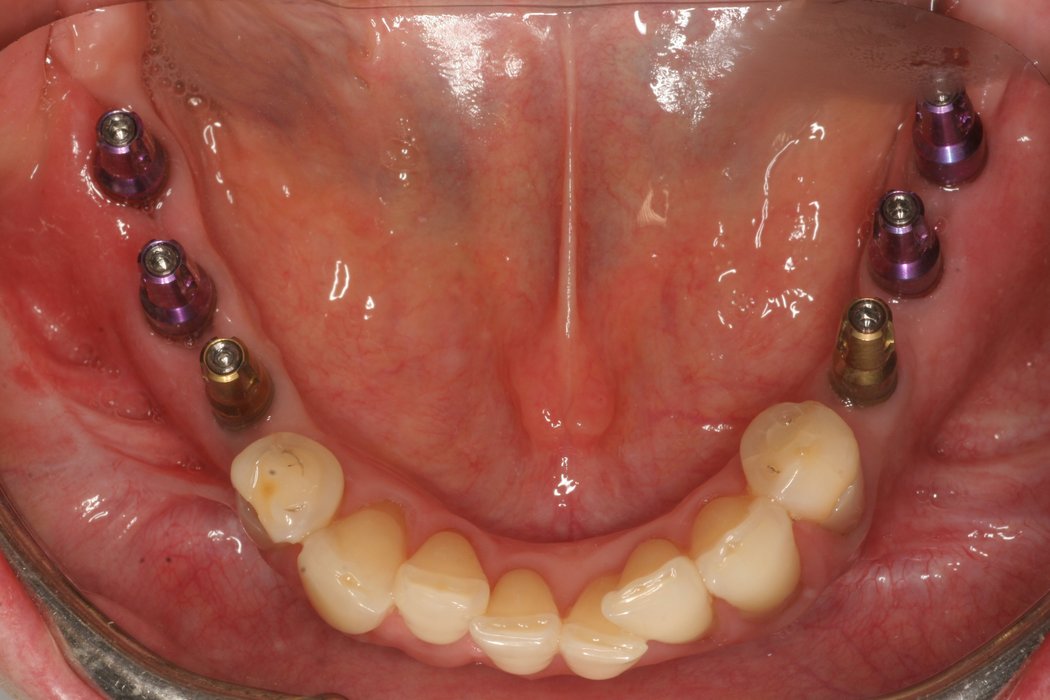
Horizontal bone augmentation
Successful placement of implants in complete or partly edentulous patients requires sufficient alveolar ridge width. Horizontal bone augmentation increases ridge width.
Conventional approaches include screwing an autogenous bone block into remaining lingual/palatinal walls or stimulating new bone formation under form-stable membranes.
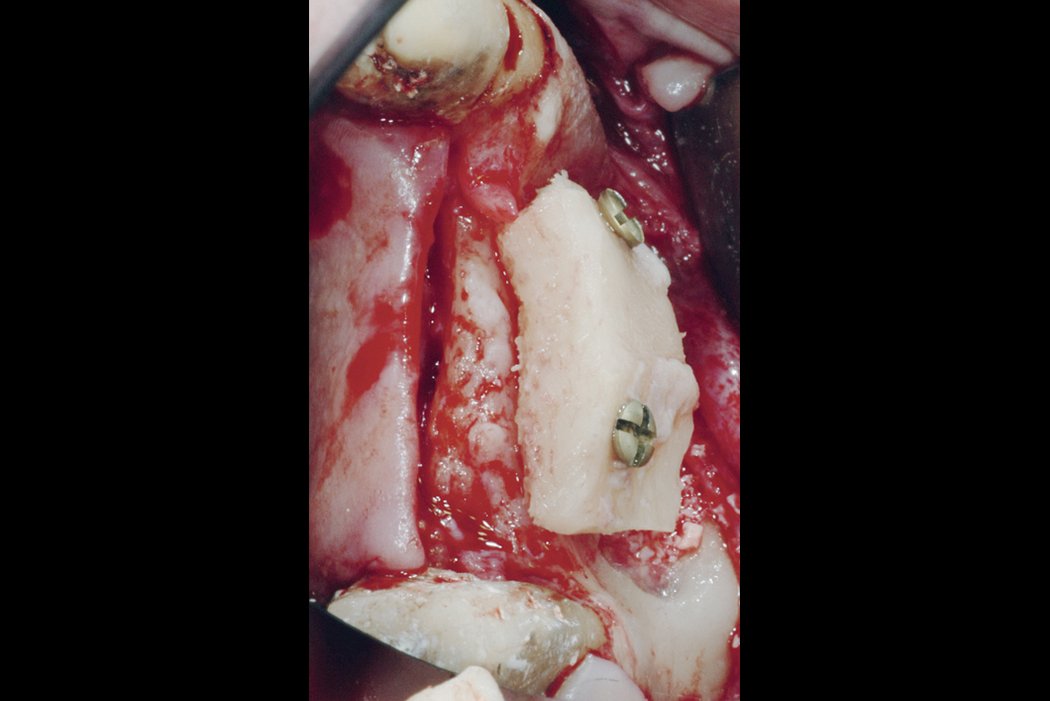
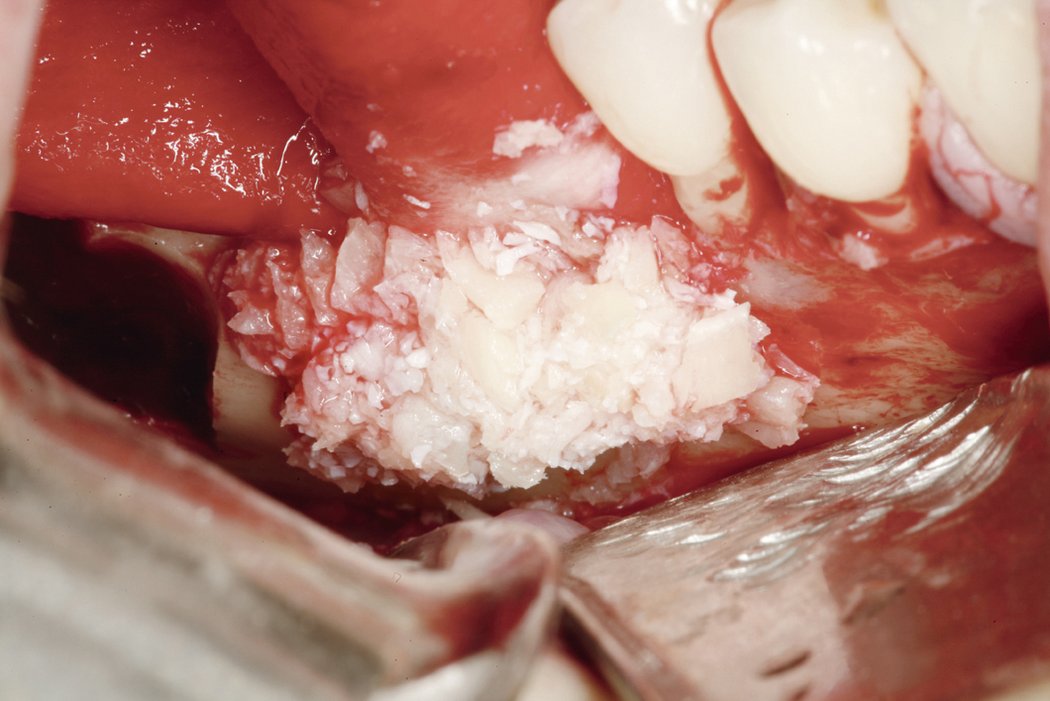
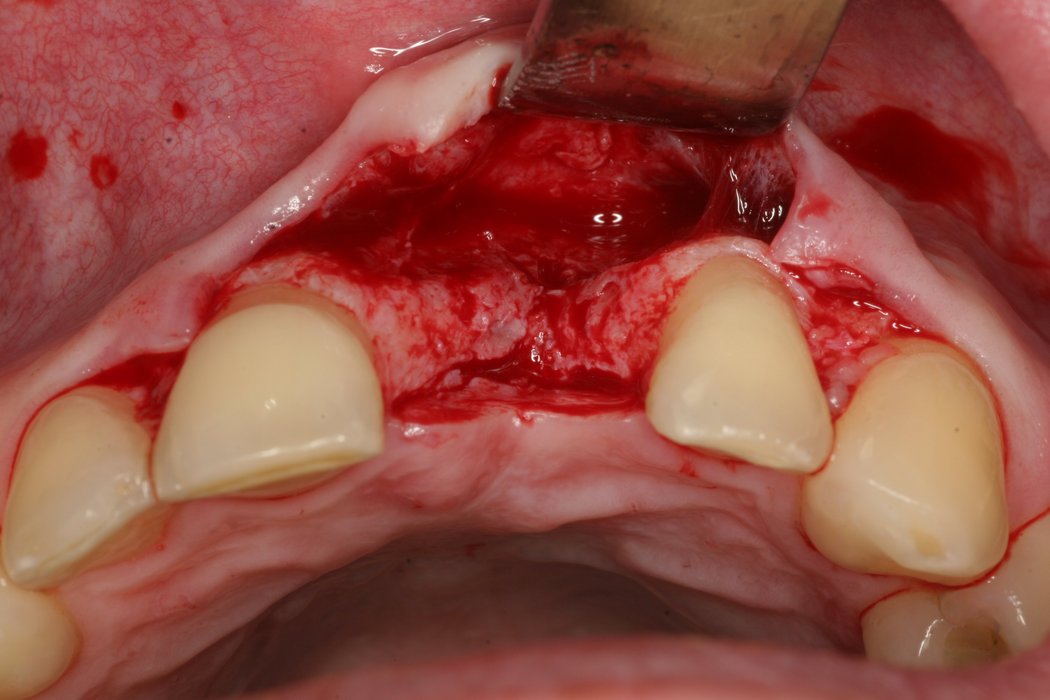
Autogenous bone blocks
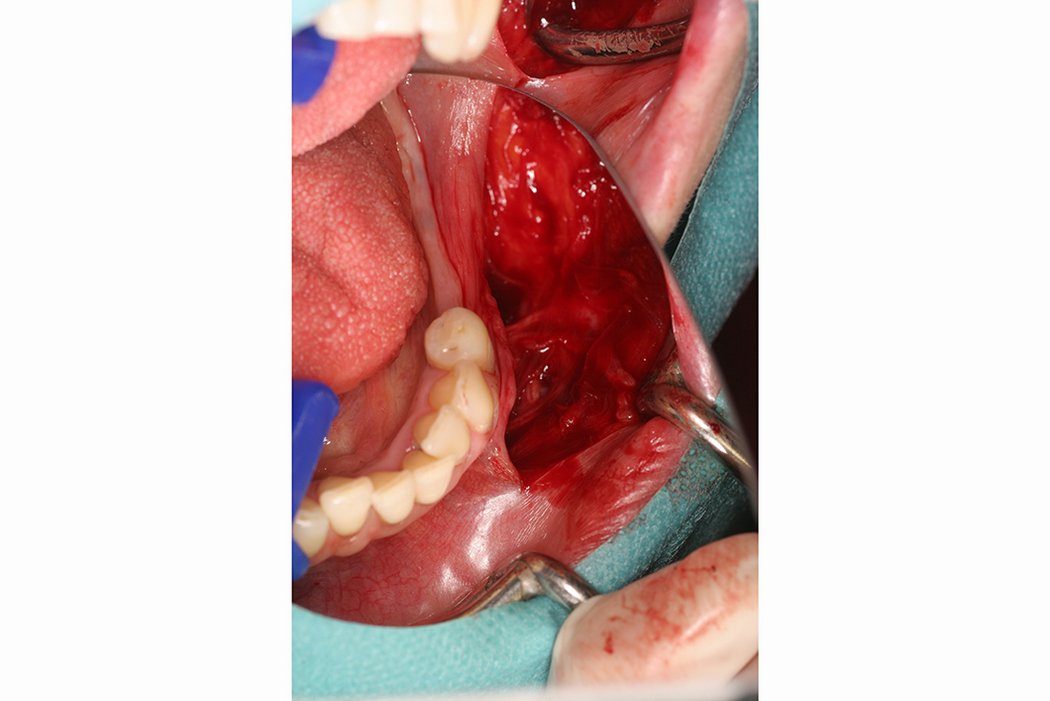
Autogenous bone blocks are the material of choice to compensate insufficient bone width. Extensive resorption, however, can result in functional and aesthetic failures1.
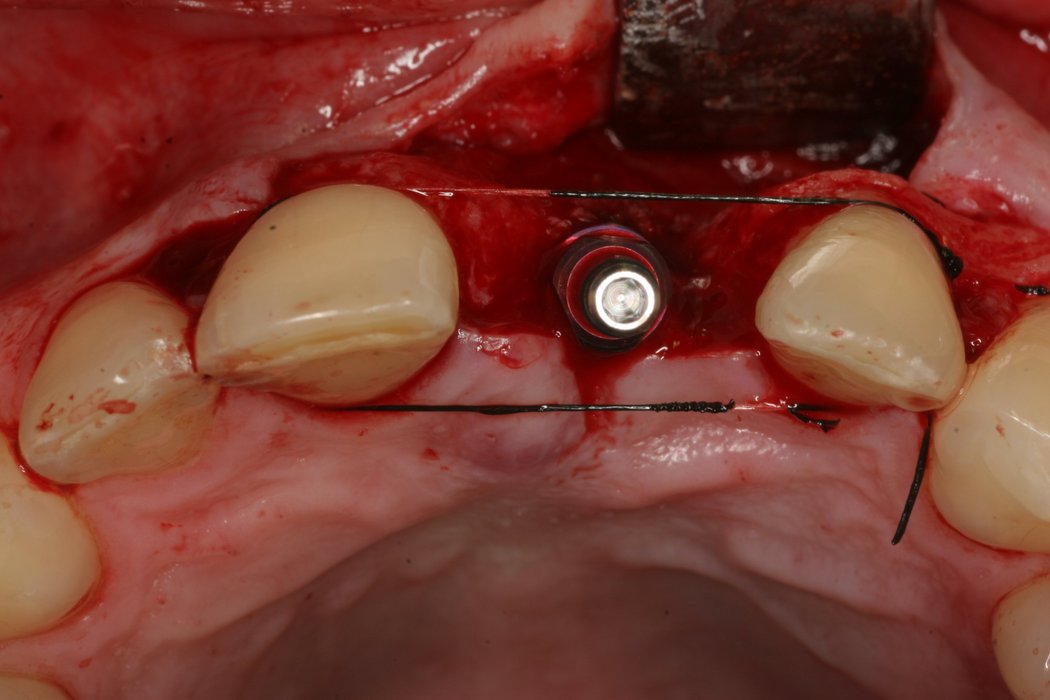
Contouring the bone block with Geistlich Bio-Oss® and covering the augmented area with Geistlich Bio-Gide® considerably reduces graft shrinkage2.
Form-stable membranes
An alternative GBR approach to obtain more bone width uses form-stable titanium-reinforced membranes, which generate space for bone formation1. However, due to their material properties they are associated with impaired healing of the overlaying soft tissue and are non-resorbable, so require a second surgery for their removal2.
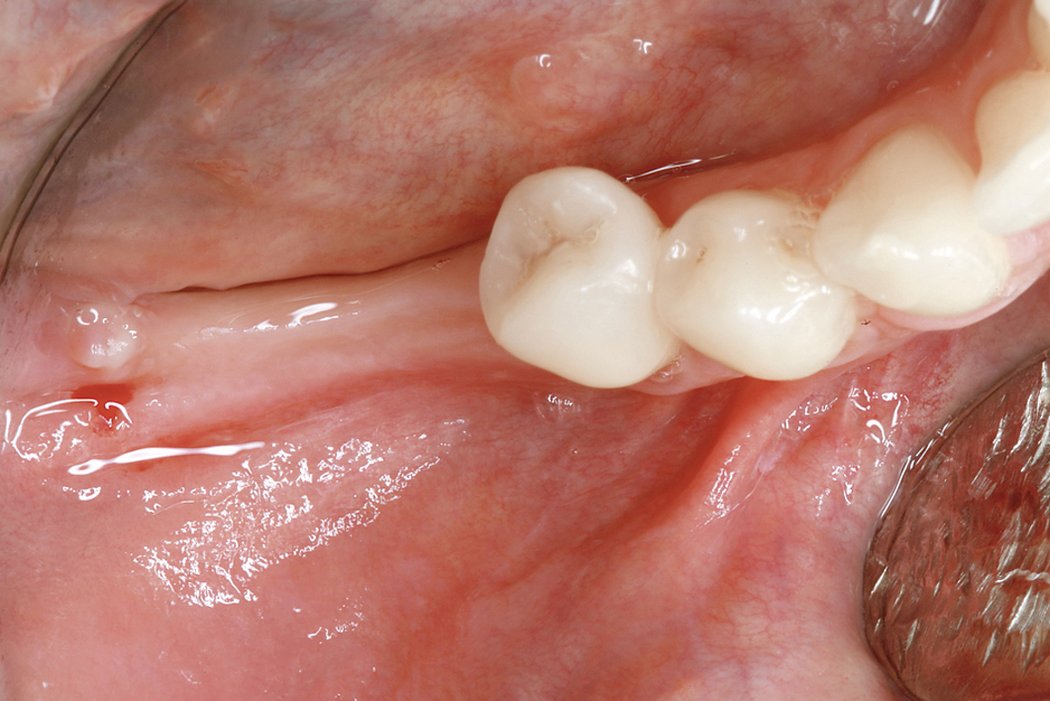
In order to overcome this complication, Geistlich Bio-Gide® can be used to completely immobilise and protect a particulated bone graft, thus leading to horizontal augmentations3:
- Geistlich Bio-Gide® is fixed securely with pins on the lingual/palatinal and buccal side
- Packed compactly with autogenous bone chips and Geistlich Bio-Oss® granules, creating a sausage skin effect
- Graft material is completely immobilised and stable
References:
- Schlegel KA et al.: Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2003 Jan–Feb;18(1):53–8 (Preclinical study).
- Jensen T et al., Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012 Mar;23(3):263–73 (Clinical study).
- Proussaefs P, et al.: Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2002; 17(2): 238-48 (Clinical study).
Geistlich Bio-Gide® collagen membrane provides a viable replacement for non-resorbable barriers and does not require secondary surgery.
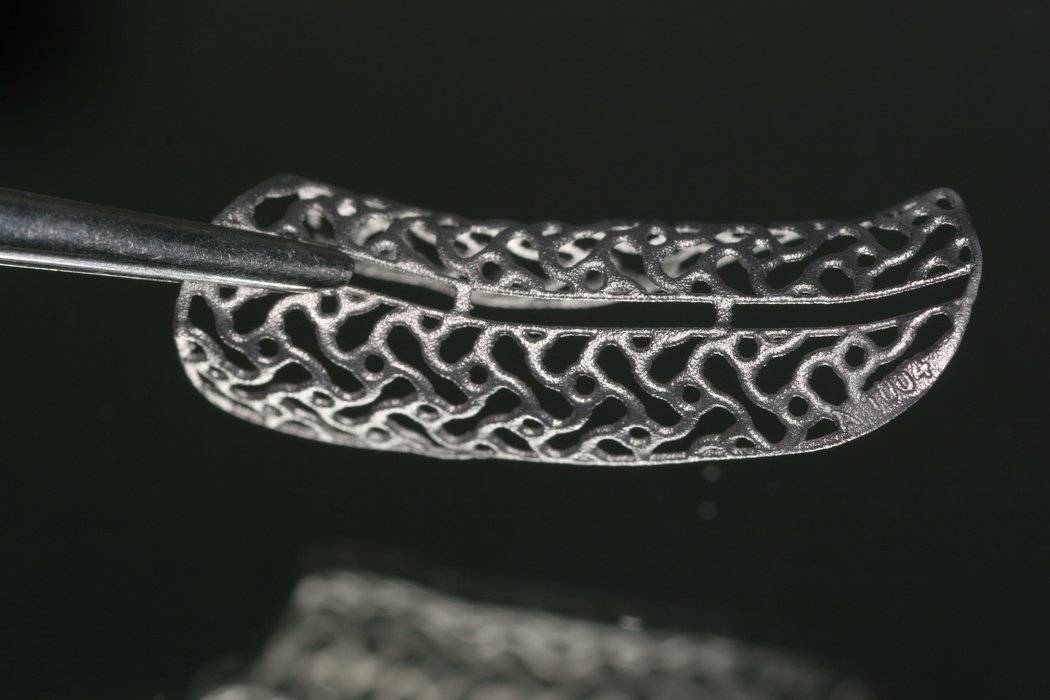
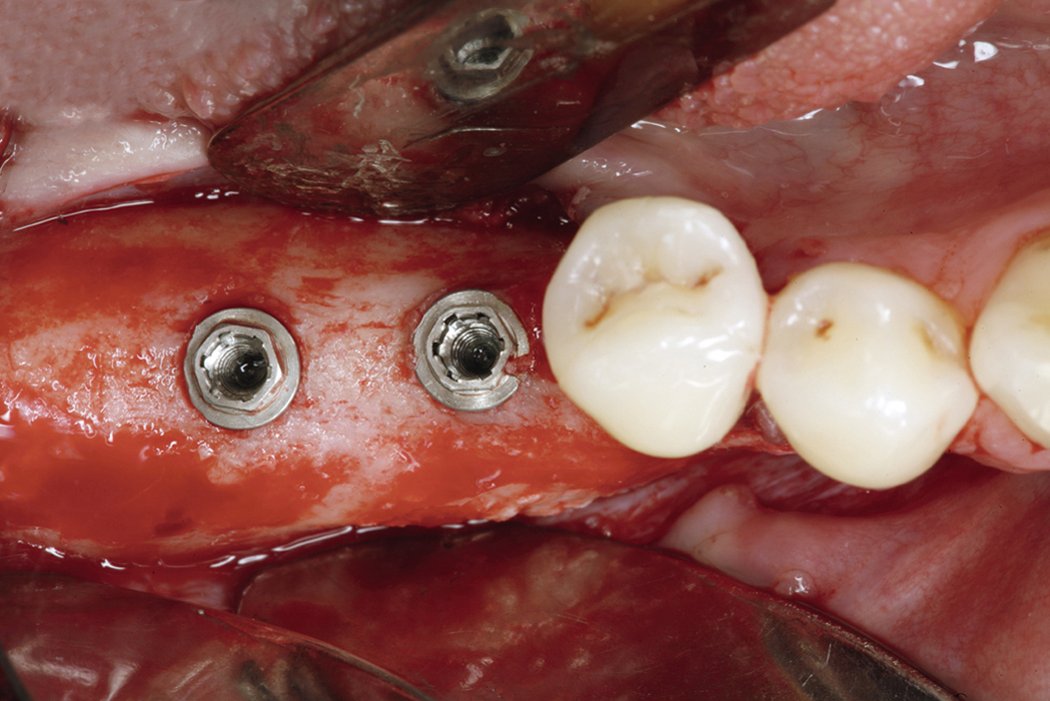
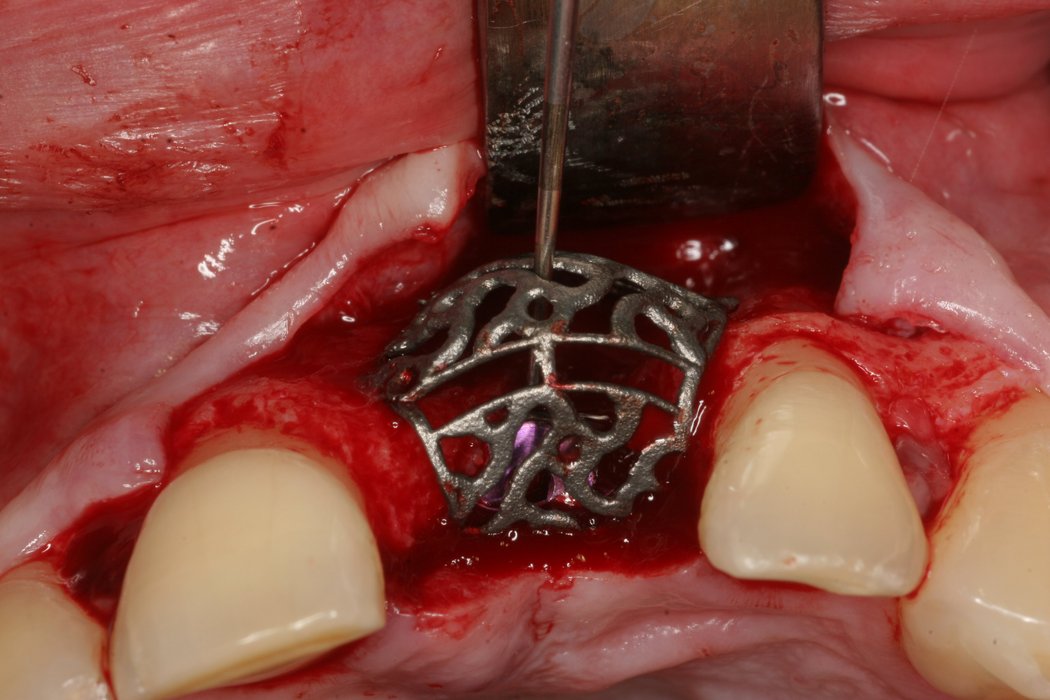
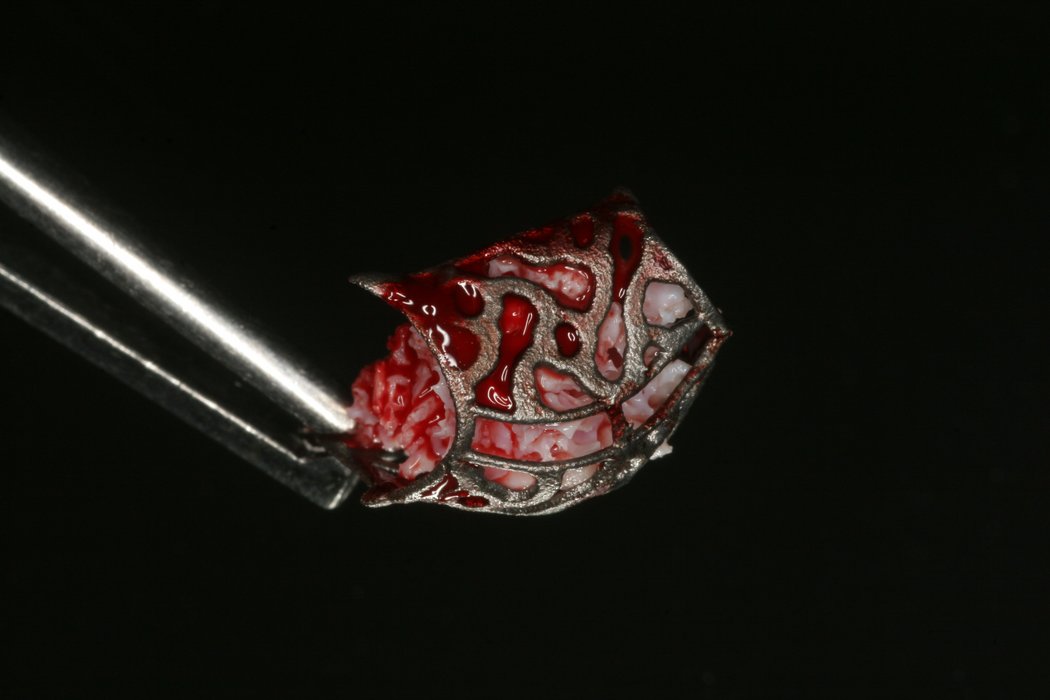
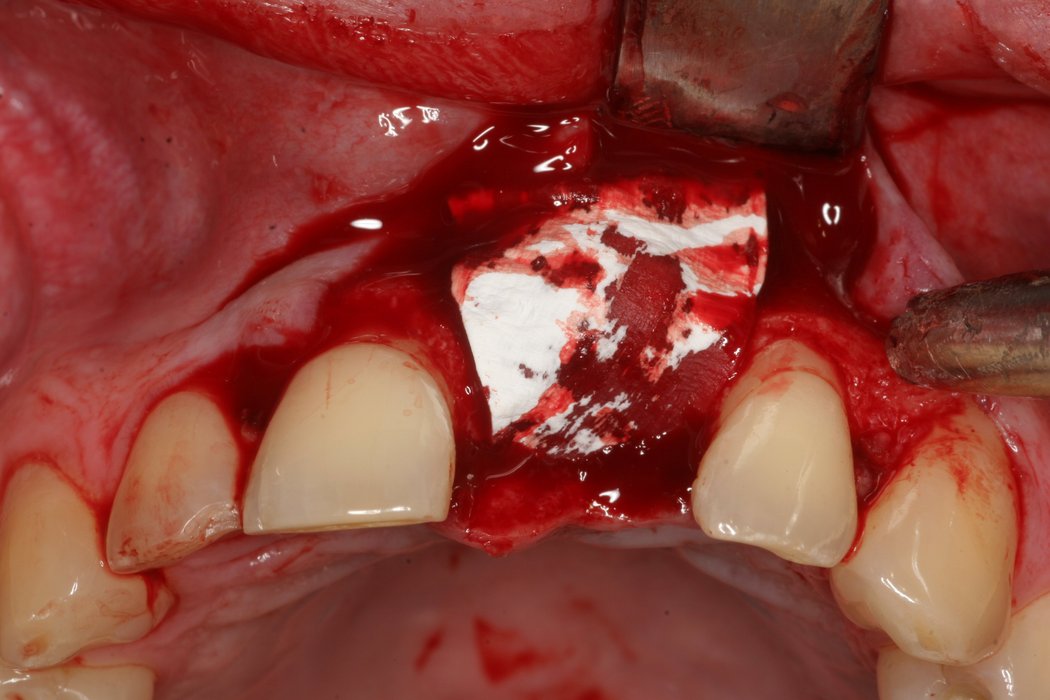
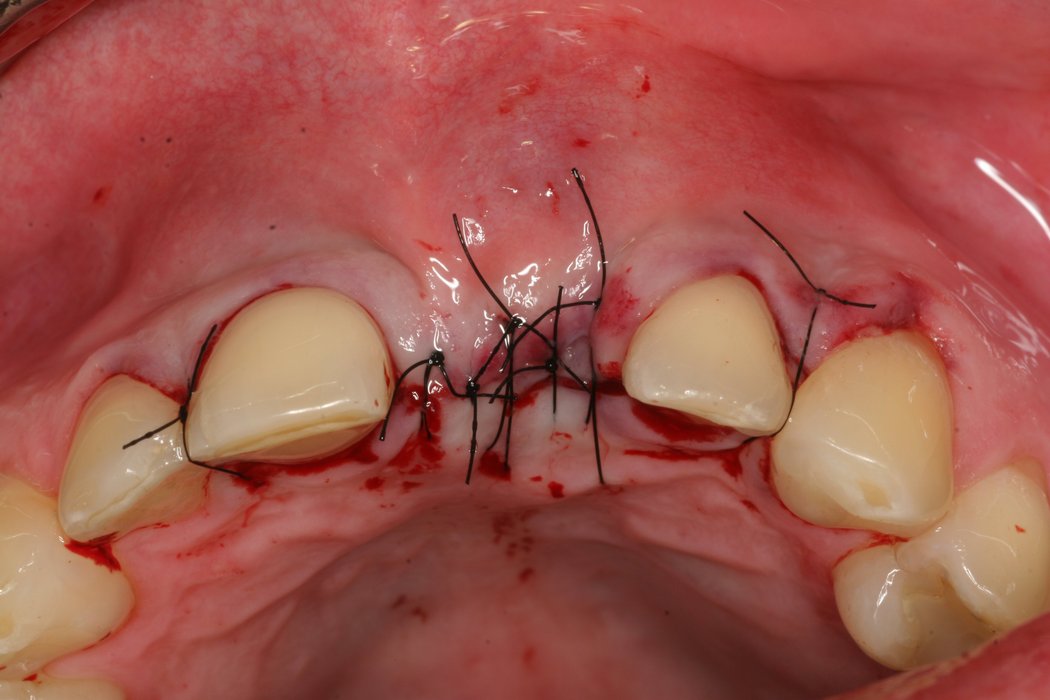
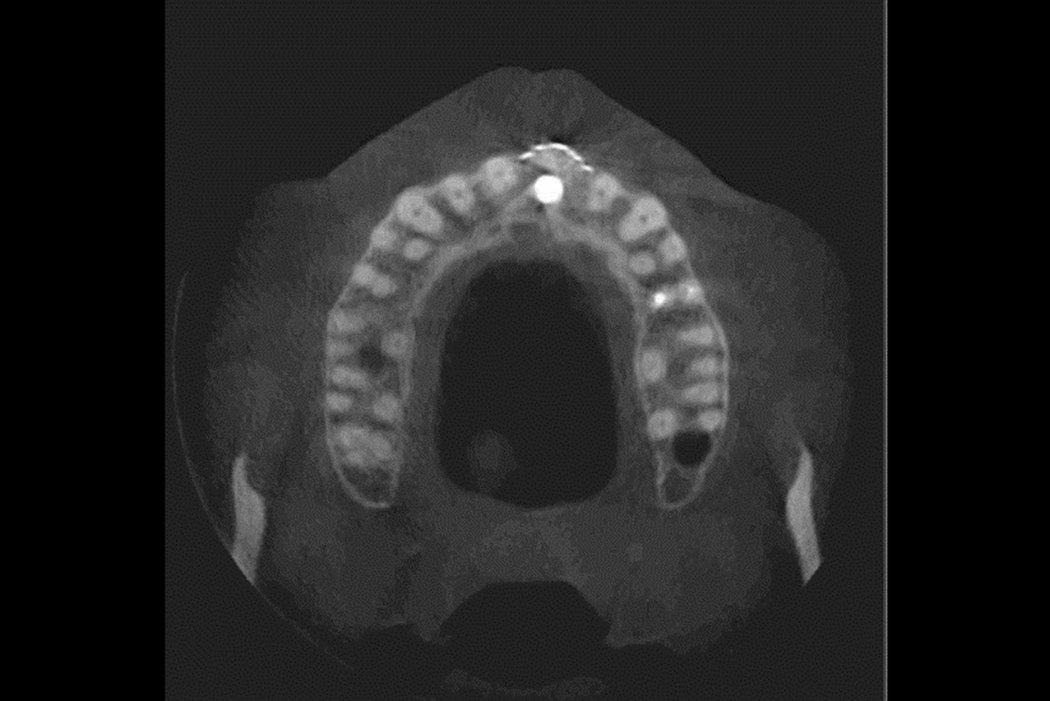
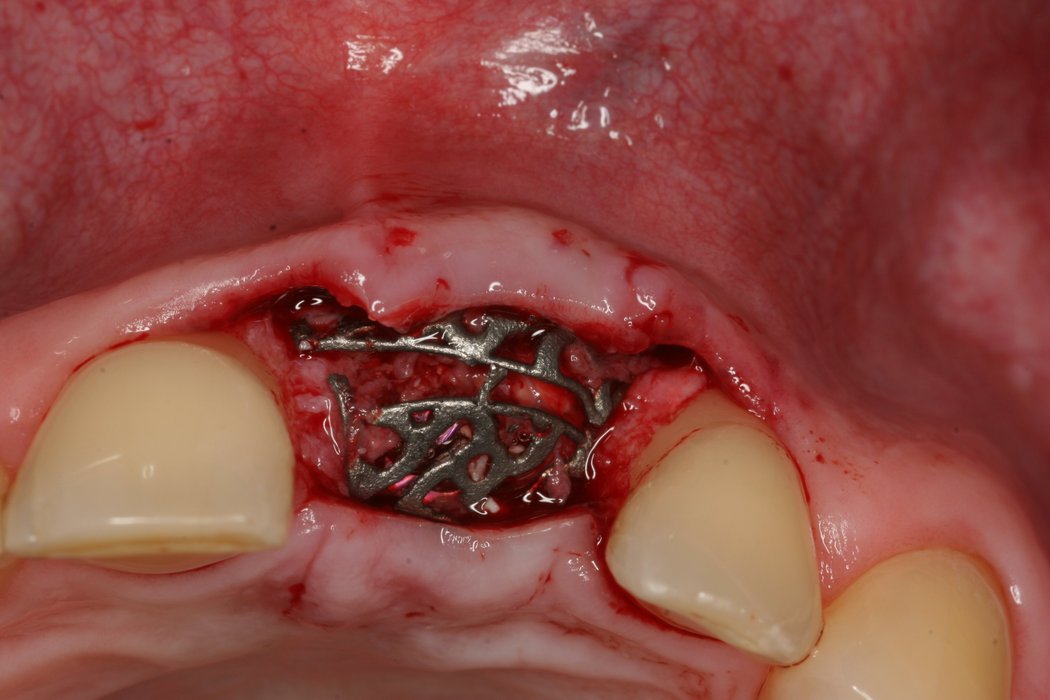
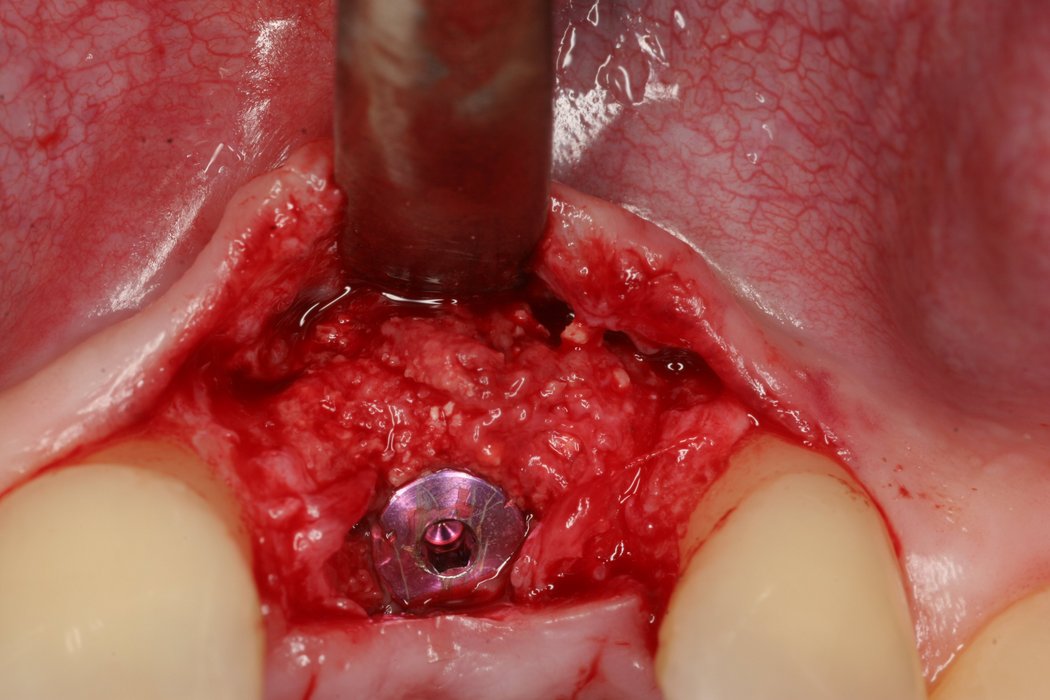
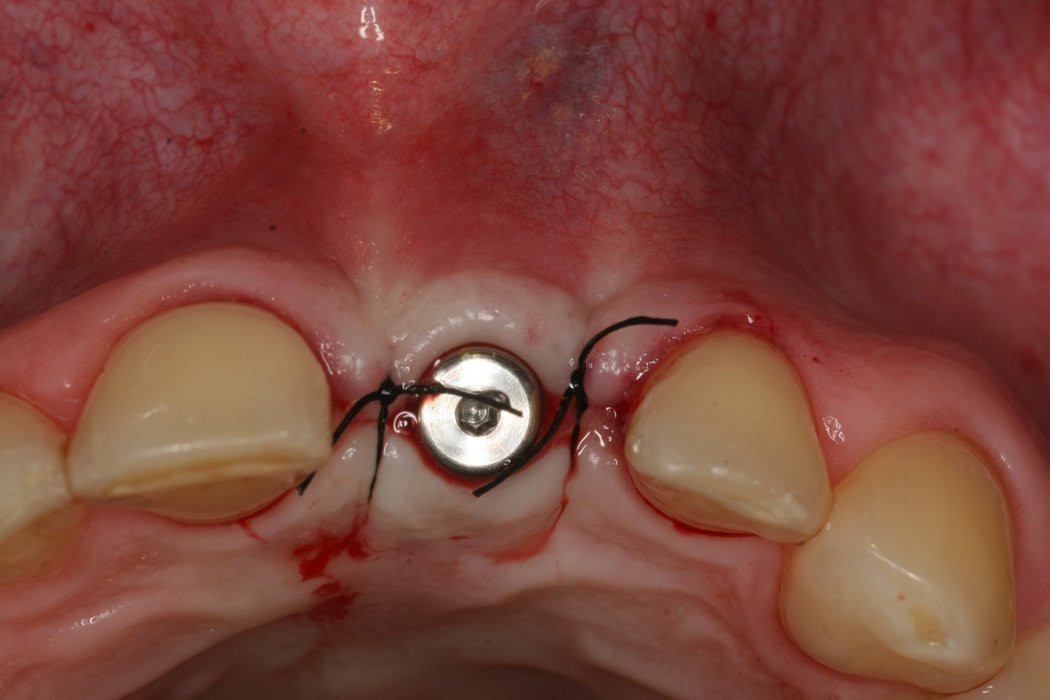
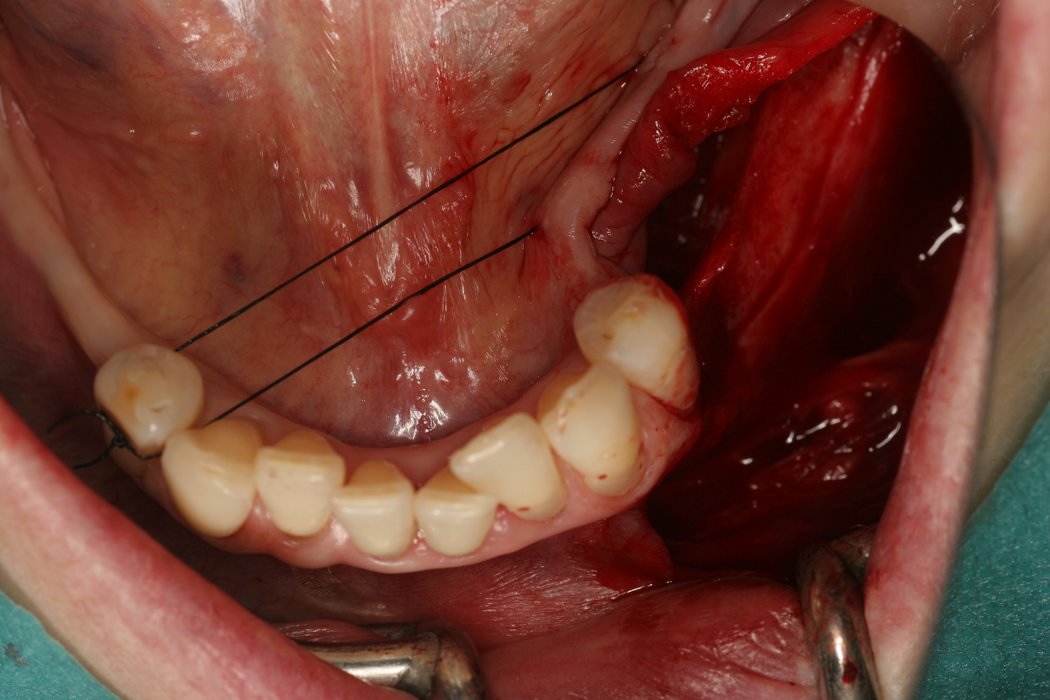
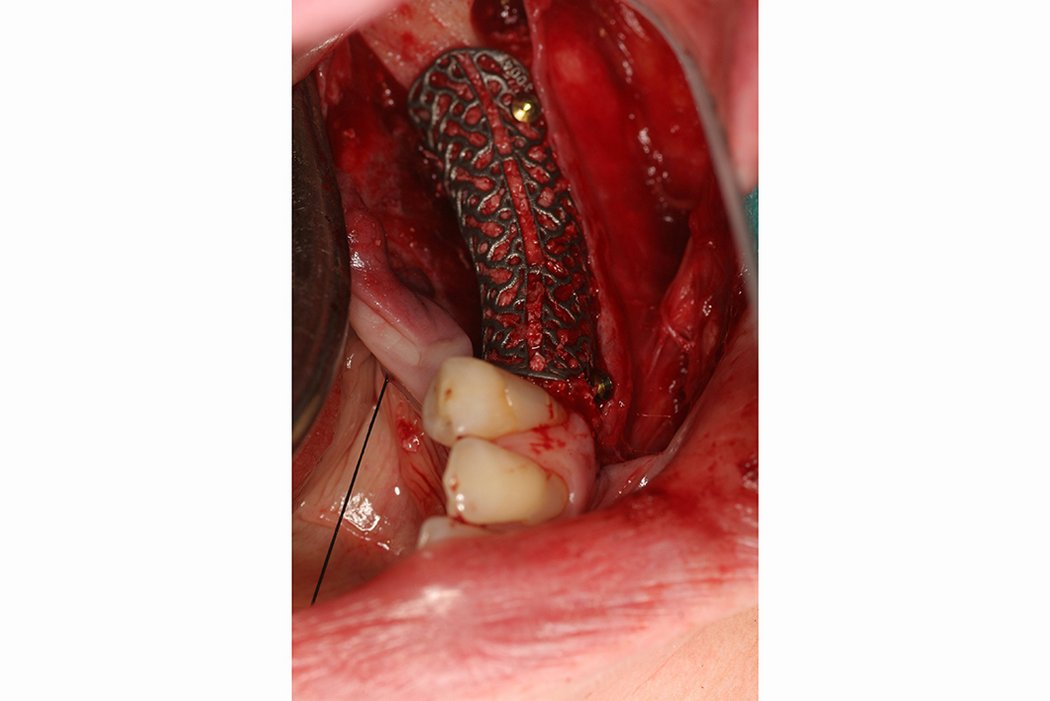
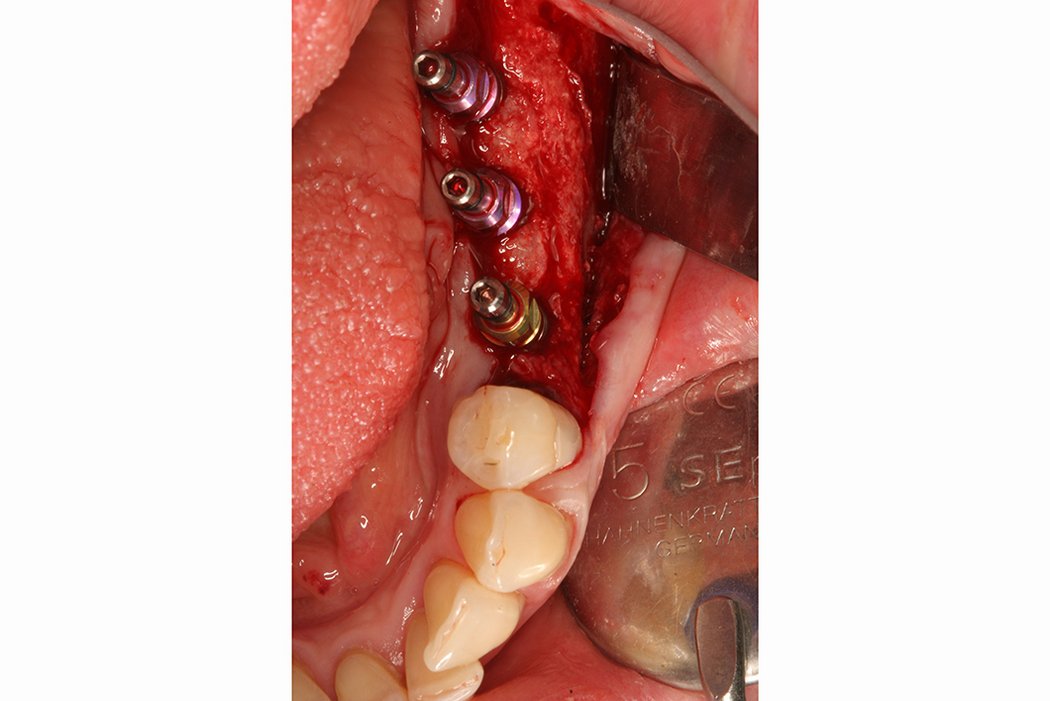
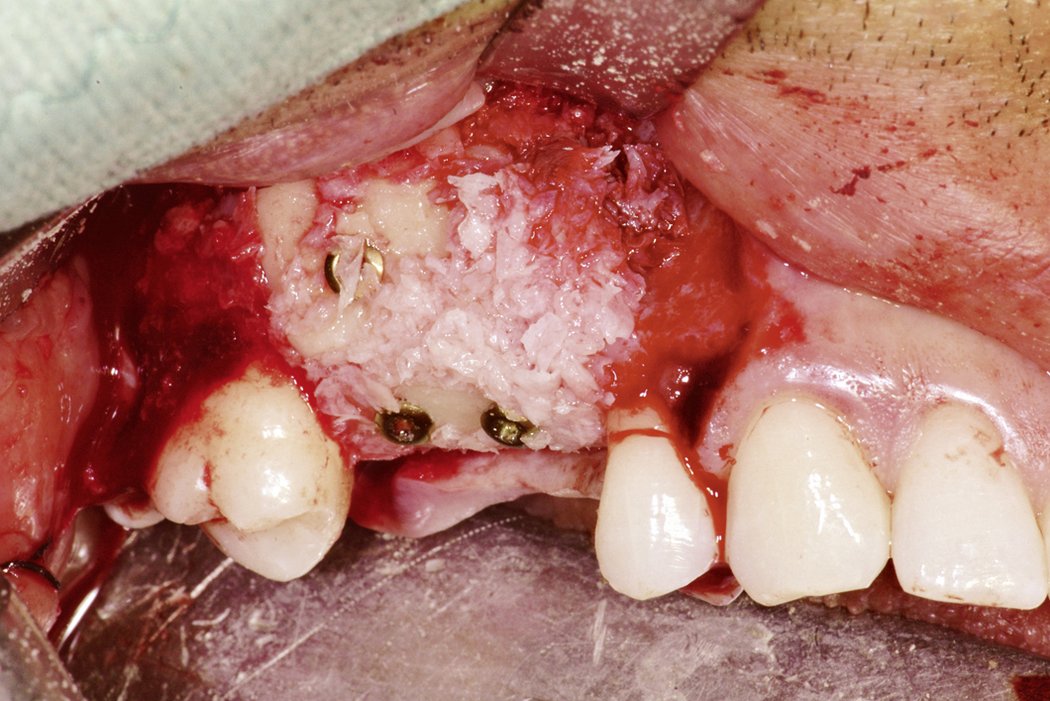
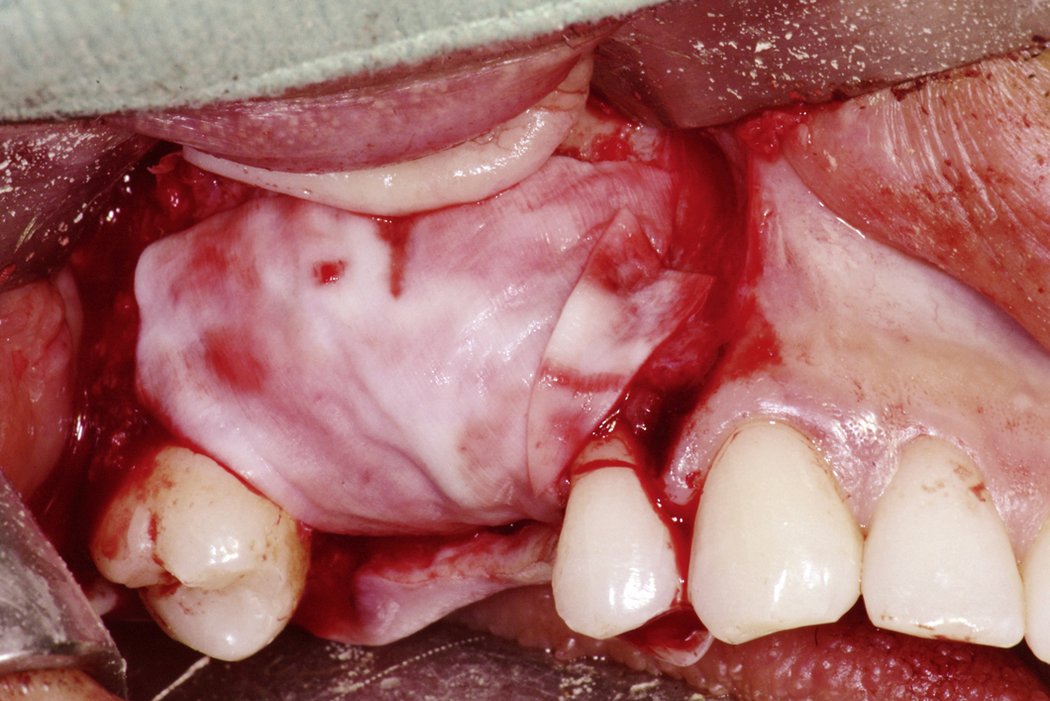
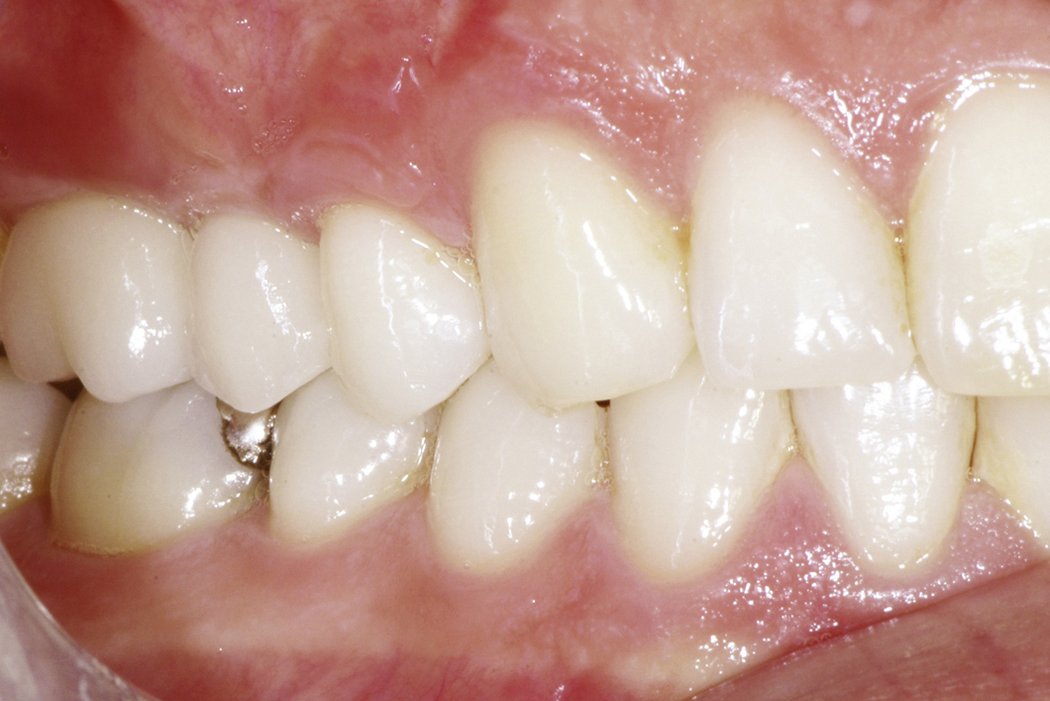
Yxoss CBR® - Individually made 3D Titanium Mesh (Case 1)
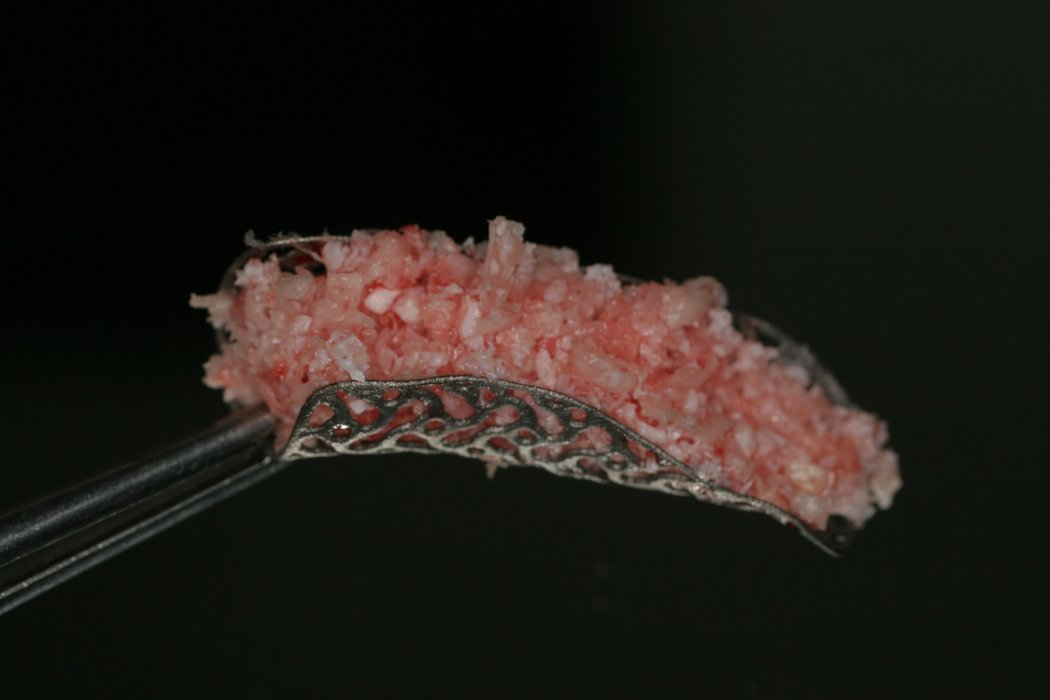
Larger and complex augmentations, especially with a combined horizontal-vertical defect morphology, still present a major surgical challenge. In these cases, the augmentation material requires a high level of regenerative ability, which can be achieved by mixing Geistlich Bio-Oss® and autologous bone. In addition, long-term stabilization of the augmentation material is necessary, which the ReOss® Customized Bone Regeneration (Yxoss CBR®) mesh structure can provide. The aim of this technique is to use the tried and tested material titanium in combination with modern CAD/CAM technology to achieve defect-specific, customized bone regeneration.
Advantages of Yxoss CBR® compared to conventional titanium mesh or titanium-reinforced membranes:
- Customizing can lead to a shortened operation time and fewer complications, as there are no sharp edges or restoring forces.
- Easier fixation - with one or two screws as needed - which is also possible in the coronal area.
- Incorporating a pre-determined break point also makes removal of the titanium mesh easier.
- The augmentation material can be determined individually in relation to autogenous bone and bone replacement.
References:
- Maiorana C, et al. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2005 Feb;25(1):19–25 (Clinical study).
- Maiorana C, et al.: Open Dent J. 2011 Apr 25;5:71-8 (Clinical study).
- Schlegel KA et al.: Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2003 Jan–Feb;18(1):53–8 (Preclinical study).
- Jensen T et al., Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012 Mar;23(3):263–73 (Clinical study).
- Proussaefs P, et al.: Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2002; 17(2): 238-48 (Clinical study).
- Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2006 Feb;26(1):43-51 (Clinical study).
- von Arx T, Buser D: Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006 Aug;17(4):359–66 (Clinical study).
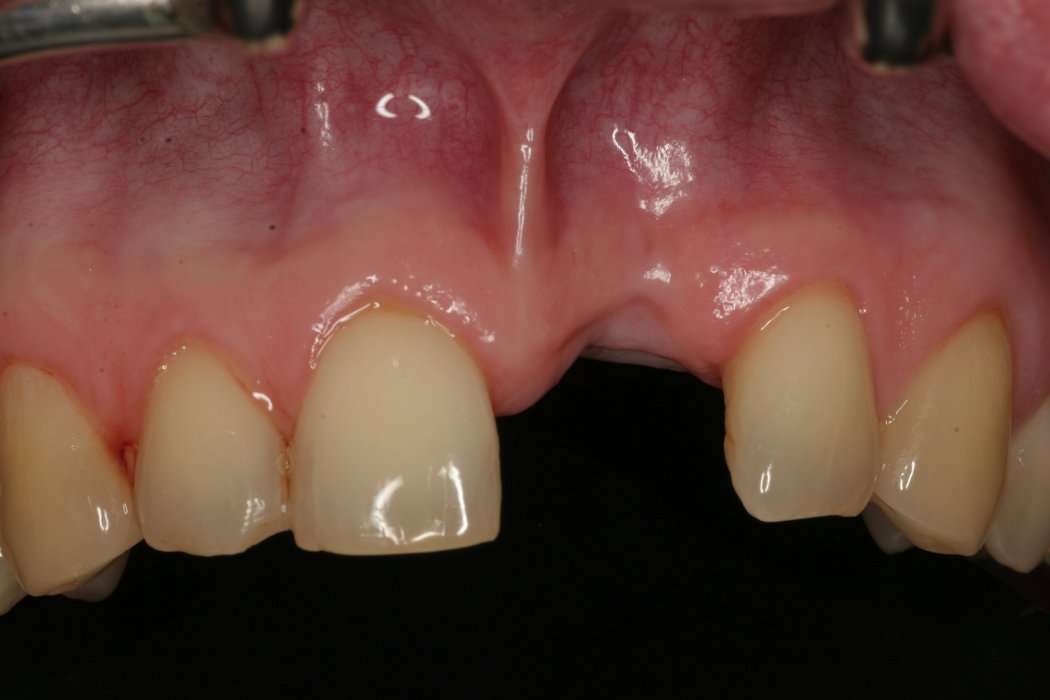
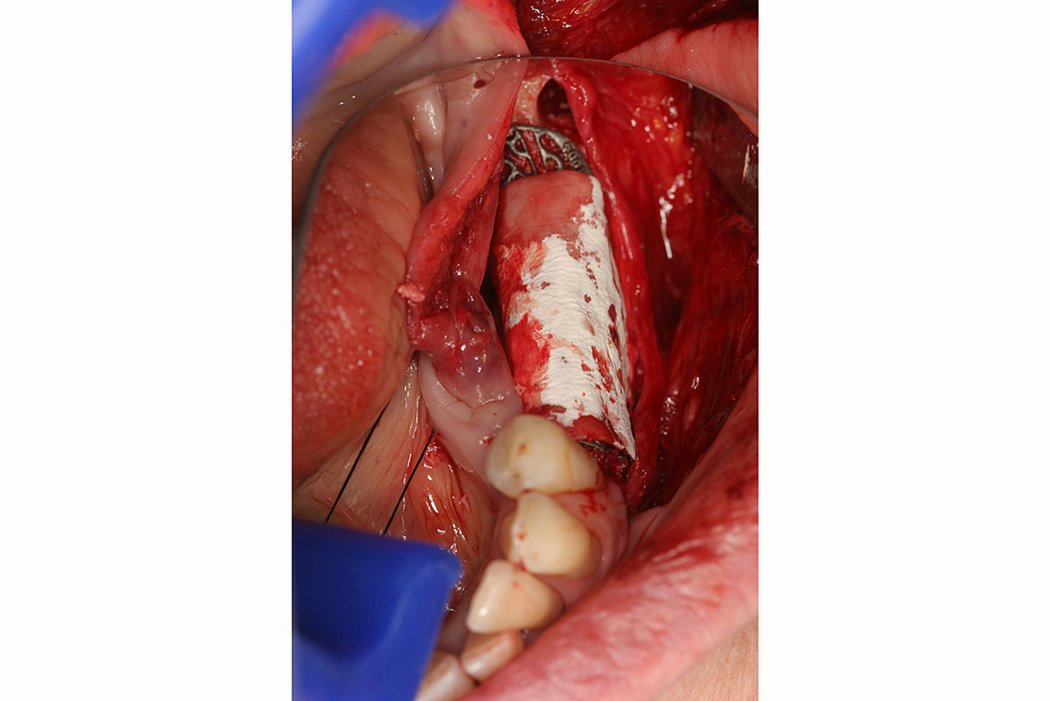
Yxoss CBR® - Individually made 3D Titanium Mesh (Case 2)
Larger and complex augmentations, especially with a combined horizontal-vertical defect morphology, still present a major surgical challenge. In these cases, the augmentation material requires a high level of regenerative ability, which can be achieved by mixing Geistlich Bio-Oss® and autologous bone. In addition, long-term stabilization of the augmentation material is necessary, which the ReOss® Customized Bone Regeneration (Yxoss CBR®) mesh structure can provide. The aim of this technique is to use the tried and tested material titanium in combination with modern CAD/CAM technology to achieve defect-specific, customized bone regeneration.
Advantages of Yxoss CBR® compared to conventional titanium mesh or titanium-reinforced membranes:
- Customizing can lead to a shortened operation time and fewer complications, as there are no sharp edges or restoring forces.
- Easier fixation - with one or two screws as needed - which is also possible in the coronal area.
- Incorporating a pre-determined break point also makes removal of the titanium mesh easier.
- The augmentation material can be determined individually in relation to autogenous bone and bone replacement.
References:
- Chiapasco M, et al.: Clin Oral Implants Res 2013; 23(9): 1012-21.
- Zitzmann N, et al.: Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1997; 12(6): 844-52.
- Schneider D, et al.: Clin Oral Implants Res 2013; Feb 25. [Epub ahead of print].
- Tal H, et al.: Clin Oral Implants Res 2008; 19(3): 295-302.
- Simion M, et al.: Clin Oral Implants Res 2007; 18(5): 620-29.
Vertical bone augmentation
Successful placement of implants requires sufficient alveolar ridge height. Conventional approaches to increase the ridge height include autogenous bone block grafting, interpositional bone grafting, and form-stable membranes.
Augmentation with bone blocks
Autogenous bone blocks are the material of choice to compensate insufficient bone height. Resorption, however, can result in functional and aesthetic complications.
Contouring the bone block with slow resorbing Geistlich Bio-Oss® bone substitute and covering the augmented area with a Geistlich Bio-Gide® collagen barrier reduces graft shrinkage. The volume of the augmented ridge remains stable1.